Japan Securities Finance
Japan Securities Finance’s Yutaka Okada, senior managing executive officer, shares with SFT the significance of its findings on the use of distributed ledger technology in the securities finance market
Japan Securities Finance (JSF) has contributed to the development of Japanese securities and financial markets for a number of years as the only securities finance company in Japan. Being aware of its public role as an infrastructure in the markets, JSF is also striving to enlarge its frontier and has engaged in empirical research in how distributed ledger technology (DLT) can be applied in securities financing.
As a securities finance company, how does the service JSF provides contribute to the market?
JSF is a securities finance company licensed under the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act and was established in 1950. Through our core loans for margin transactions business, we have played an infrastructure role for the Japanese securities market, especially in providing liquidity as a lender of last resort for the stock market for more than 70 years, while developing various services related to securities finance to meet diverse client needs.
What initiatives are JSF undertaking with respect to the use of DLT?
In collaboration with the Graduate School of Engineering of The University of Tokyo, Laboratory of Professor Kenji Tanaka, we conducted empirical research to explore the feasibility of using DLT to facilitate securities financing transactions (SFTs) and released a report compiling the results on 30 May 2023.
Looking at the scale of SFTs in Japan, the balance stood at around JPY 200 trillion. However, there has been little research using DLT in Japan focusing on SFTs. It would be very valuable to explore the feasibility of using digital tokens in SFTs, which are essential for providing liquidity to the market. JSF therefore decided to conduct this empirical research.
How did you carry out this research and what were the key findings?
The empirical research addressed three key points of inquiry.
The first was the feasibility of SFT execution with regards to individual bilateral transactions. JSF tested whether various types of SFTs, including those involving the exchange of assets denominated in different currencies, can be smoothly implemented from the start of transactions through margin calls to the end of transactions. In addition to the exchange of security against cash (typical repo), we also tested the exchange of security against security.
The second evaluation focused on the system performance when processing transactions on a market-wide scale. Transactions that occur in the entire market were input into the system and its performance was evaluated. We analysed how resilient the developed system is in terms of a high concentration of transactions during market stress or recovery from system disruptions. In addition, we measured how resilient it is to the anticipated large system workload when marking to market and implementing margin calls every business day, where the system burden is considered to be heavy.
The third research focus involved the impact of collateral diversification and threshold setting for margin calls on net credit amount and necessary liquidity, including the impact in times of market turmoil.
We conducted simulations for each market scenario — normal time and market turmoil including rapid increase, rapid decrease and high volatility — depending on how diverse collateral is and whether or not a threshold is set when implementing a margin call.
What implications were identified within your research and what are the advantages of using tokenised assets for SFTs?
From this research, we drew five principal conclusions.
Transaction feasibility
We confirmed that various types of SFTs can be smoothly implemented from the start of transactions through margin calls to the end of transactions.
With regard to the start of transactions, the recording and approval process was carried out smoothly even in times of market stress when the daily market-wide transactions were concentrated in one hour. Mark-to-market and margin call processing were possible, although it took a certain period of time even when assuming that one-third of outstanding transactions that exist in the entire market are concentrated.
Fig 1: Conceptual diagram of empirical research
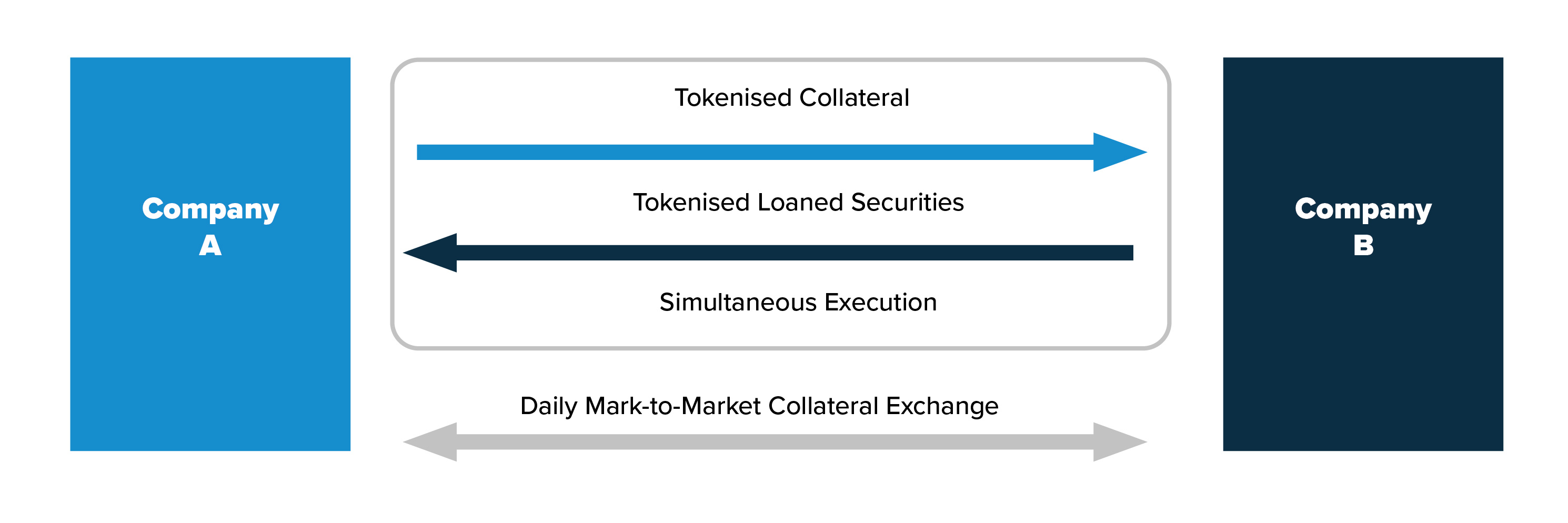
Reduction of settlement risks and simultaneous execution of transactions denominated in different currencies
Blockchain technology can be utilised to exchange tokens for tokens simultaneously without a time difference. In the case of exchanges in existing settlement systems, which involve foreign currencies or foreign securities, the transfer of funds and securities must be executed during local time at the local transfer institution. For this reason, generally a time difference occurs before completion of transaction settlement or completion of margin call.
In this empirical research, on recording and approving the transaction on the blockchain after deal, the exchange of tokens for tokens on the blockchain could be executed simultaneously in real time — even if the underlying assets are denominated in different currencies. Also, margin calls can be automatically implemented after updating the daily market value without the need for operations by the transaction parties.
Reduction of credit risk and flexibility in economising liquidity
The project confirmed that automation of margin calls using blockchain technology reduces operational burden, making it easier to make margin calls and, as a result, this can also reduce credit risk.
Automation can almost eliminate the operational burden involved in managing collateral diversification and adjusting multiple assets posted as collaterals in margin calls. As a result, collateral diversification reduces volatility not only in collateral value but also in net credit amount, having a positive effect on credit risk management. In cases where a threshold is set to reduce operational burden associated with margin calls, the automation offered through blockchain and smart contracts is itself important in relieving the operational burden. Therefore, threshold setting also provides the benefit of controlling system burden following an increase in the number of margin calls.
When a threshold is set, margin calls will not be executed until the net credit amount reaches the threshold. Therefore, the net credit amount will increase compared to when no threshold is set. We confirmed that this effect can be mitigated or offset by diversifying the collateral securities.
Furthermore, the credit risk reduction effect and liquidity economising effect gained through such a combination of the threshold and collateral diversification effect proved to be particularly effective during market turmoil.
Streamlining of operations
Using blockchain in SFTs enables automated execution without manual intervention following predetermined conditions in a smart contract with regard to settlements. This captures details related to the start and end of the transaction and margin calls during the transaction term.
These results suggest that the use of blockchain can make it possible for straight-through processing (STP), improving the efficiency of SFT operations and managing operational risks. In particular, this has the potential to significantly reduce the operational overhead and time required to exchange transaction information and check execution status with counterparties located in foreign countries, thereby improving the efficiency of transactions.
Utilisation of assets with low liquidity
There are cases where the transfer of the rights of certain securities with low liquidity, such as unlisted shares, involves a significant operational burden and time as the actual certificate must be transferred or changes must be made to the registry. It will become easier to transfer rights of low-liquidity assets by tokenisation. This provides potential not only to hold these low-liquidity assets, but also to utilise them as collateral in SFTs. Furthermore, it is believed that increasing the usage as collateral in this manner has the potential to increase the valuation of the underlying assets.
The results of this research are published in a paper entitled “Empirical Research on SFTs using Distributed Ledger Technology” (https://www.jsf.co.jp/english/media/report_dlt_en.pdf).
What future initiatives do you have in the pipeline for the use of DLT in SFTs?
Through this research, we found that there are various possibilities for utilising blockchain to support SFTs. Although there are issues to be addressed, such as connection to external systems and handling of legal considerations, we aim to explore the possibility of conducting actual transactions on a trial basis.
Is there anything else you would like to share with our readers?
In November 2023, JSF formulated and published the Long-Term Management Vision, which includes the corporate message “Be unique. Be a pioneer”. In the field of DLT, we aim and strive to be unique and a pioneer.
We also proactively participate in international conferences organised by the International Securities Lending Association (ISLA) and the Pan Asia Securities Lending Association (PASLA). We look forward to engaging in exciting discussions with market participants on such occasions.


